Definition of Charge and Its Properties
Charges and Interactions
Definition and Basic properties of Charges
Path of Charged Particles
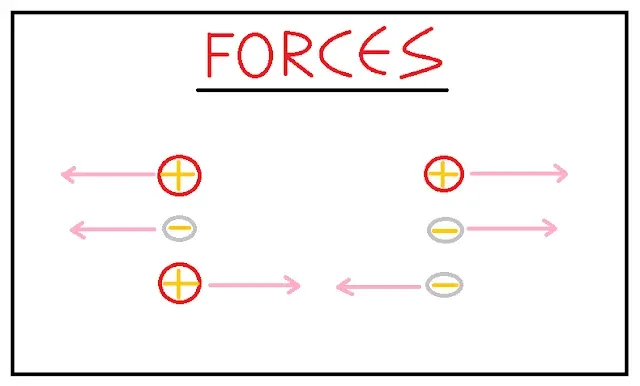
Forces
Atomic Concept (meaning of a Charged body)
Methods of Charging
By Friction
By Induction
Electroscope
Here's a fun task for the readers to do
Charges and Interactions
Definition and Basic Properties of Charges
Charge or Electric Charge is the materialistic property of a matter or if we go even deep at the level of atoms and molecules we can define it as the property of the constituent particles i.e protons, electrons and neutrons.
More precisely, charge is that fundamental property owned by Protons, Electrons or Neutrons.
Same types of charges repel each other while unlike charges attracts as shown in the above figure.
The charges are neither positive nor negative, it is only a convention to differentiate their interactions in different types of conditions.
Path of Charged Particles
Que> Have you ever thought about the path of these charged particles as when it flows as a current in a wire or lightning bolts (generally I am talking about electrons) during thunderstorms?
Ans> From our childhood teachers told us that electric current contains electrons that flow in a straight line at a very high speed. But electrons flow in a wave-like pattern and therefore charged particles also flow in the form of waves.
Note: Charge is a scalar quantity while interactions like force between charges is a vector quantity.
Forces
According to the situation that whether charged particle is on rest or moving, forces can be classified into two types:
- Electrostatic Force: The force exerted by charged particles when they are at rest or stationary falls in this type.
- Electromagnetic Force: The force exerted by two moving charged particles falls under this type.
- Electrostatic Force: If we consider only an instant of time both the charged particles are at rest, at those instants the interaction between the two particles is of electrostatic type.
- Magnetic Force: This is a special property of charged particles that when they are in motion they produce fields around them in 3D space similar to magnetic fields. This field produces force and due to its interference in exerting force, force produced by moving particles is known as Electromagnetic Force.
Note: Magnetic fields are different from electric fields. Electric fields are also possessed by static charges.
Electromagnetic Force = Static force + Magnetic force.
Atomic Concept (meaning of a Charged body)
Charged body means that the proportion of protons and electrons is not the same in that body or that part of the body. Most of the bodies are neutral since atoms from which they are made up have exactly the same number of protons and electrons.
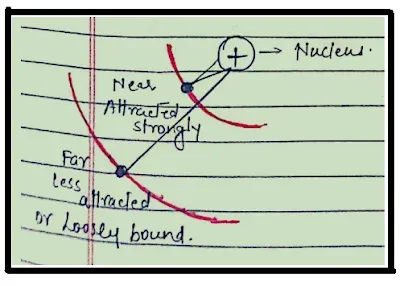
These bodies then get charged since the outermost electrons in big atoms are not tightly bound with the nucleus and can easily be taken out as shown in the figure below.
As shown in the figure, as an electron is farther from the nucleus it can be easily taken out by simply giving a small amount of energy to that electron. It means that the atom has less Ionization Enthalpy.
Methods of Charging
By Friction
When two bodies are rubbed together, due to friction electrons come out of atoms and get exchanged. Electrons transfer from one body to another and due to a net transfer of electrons, one body loses electrons and gets electron deficient while the other body gains the same number of electrons and has excess of electrons.
The body which loses electrons becomes positively charged and the body which gains excess of electrons becomes negatively charged.
The two bodies get oppositely charged due to friction and the cause due to which the property of charging is acquired is called frictional electricity.
If there is a net transfer of 'n' electrons from a body 'A' to another body 'B'.
Charge on 'A' would be q(A)= +n*e.
Charge on 'B' would be q(B)= -n*e.
e = 1.6*10**(-19) Coulomb.
'n' is equal to 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, till infinity.
By Induction
Here is no physical contact between bodies.
By Induction or Electrostatic Induction one can induce charge to a body through a charged body without making a physical contact b/w the two bodies.
In this procedure we have two bodies one is charged and the other is a conductor, the theory is simple that when we take charged body closer to the conductor, the charged body attracts attracts the oppositely charged particle to nearer end of conductor and repels same charged particle to the farther part of conductor w.r.t the charged body taken.
Steps for charging by Induction:
- Take a charged body(let for example we have taken a positively charged body) and a neutral conductor at some distance. Now bring them closer.
- Due to the positively charged body, free electrons in the conductor are attracted and move towards the charged body and accumulate at the nearer end.
- The positive charge of ions from where free electrons have been shifted, now appears at farther ends.
- Make an electrical contact of farther end with the Earth. (the symbol in 3 and 4 represents connectivity with the Earth).
- Due to earthing the positive charge goes to Earth from farther away. Only negative induced charge is left on the conductor.
- Earth is disconnected and the positively charged body is now taken away. All the induced negative charges are now distributed equally all over the surface due to mutual repulsion.
Thus, a body can get charged without being in physical contact.
Problem: How to determine which body is charged or overall neutral?
The solution to this problem is an Electroscope.
Electroscope
An Electroscope is a simple device that was developed to determine whether a body is charged or not by a simple principle named as INDUCTION of charge.
Use of gold sheets is not necessary, you can use aluminum foil also Metal ball is also not necessary, using only conductors is enough and will give good results. Use a transparent glass or any utensil as per your availability.
Working: When you take a charged body near the metallic ball or conductor the gold/aluminum sheets tend to go far from each other, this is because when the charged body comes closer to the conductor it either attracts or repels the free electrons present in the conductor.
Due to which a similar type of charge is accumulated over one end and at the side of the gold/ or aluminum sheet, since they are two halves and both acquire a similar type of charge and thus start repelling each other, this indicates that the body is charged.
Here's a fun task for the readers to do
Try to make this electroscope at your home, it can easily be made at home and then try to bring a used comb near the electroscope and see the results. Have you observed any reaction? What are your observations? What was the reason behind that? Try to explain.







What is free electron?
ReplyDeleteFree electrons are those electrons that are not tightly bounded with nucleus and moves freely throughout the body of object.
Deleteyes these are mostly seen in large atoms.
Delete